Saba’s Plan for a Coral Comeback
Saba has an exciting new initiative to restore its coral reefs. This new project, running from 2024 to 2026, will focus on reviving key species in the island’s underwater ecosystems. With a collaborative team from the Saba Conservation Foundation (SCF) and Van Hall Larenstein (VHL) University of Applied Sciences, the project aims to restore both corals as well as sea urchins.
This initiative is centered around coral restoration, specifically reviving two essential coral species—staghorn coral (Acropora cervicornis) and elkhorn coral (Acropora palmata). By mapping parent colonies and using a technique known as coral gardening, SCF will create and maintain coral nurseries. These corals will eventually be outplanted at key reef sites around Saba to not only expand the number of coral colonies, but also provide essential fish habitat. The project focusses on installing coral nurseries, training staff with the newest techniques and starting with the restoration of key reef sites.
Reef Cleaners to the Rescue
It’s not just corals getting a makeover—this project also shines a spotlight on the essential role of grazers, particularly sea urchins. VHL is leading the charge on cultivating and restocking two key sea urchin species, West Indian sea egg (Tripneustes) and long-spined sea urchin (Diadema), known for their ability to keep algae in check. By removing algae, which are important competitors of corals, they help the coral to thrive. By restoring these “reef cleaners,” Saba’s project will give corals the breathing room they need to grow, setting the stage for a healthier, more balanced marine ecosystem.
From Tiny Urchins to Big Goals
The project will be funded as part of the Dutch Government’s Nature and Environment Policy Plan (NEPP) 2020-2030 for the Caribbean Netherlands, a comprehensive initiative aimed at conserving and restoring the unique natural environments of the Dutch Caribbean islands, including Saba, St. Eustatius, and Bonaire. This project is aiming for big milestones: build and maintaining coral nurseries, the expansion of urchin cultivation facilities, and the creation of a dedicated research center. By 2026, the project hopes to ramp up coral and grazer restoration, with the ultimate goal of extending these efforts across the Dutch Caribbean. By linking local initiatives to broader regional goals, Saba’s restoration project promises to leave a lasting impact on both the environment and the community.
DCNA
The Dutch Caribbean Nature Alliance (DCNA) supports (science) communication and outreach in the Dutch Caribbean region by making nature related scientific information more widely available through amongst others the Dutch Caribbean Biodiversity Database, DCNA’s news platform BioNews and through the press. This article contains the results from several (scientific) projects but the projects themselves are not DCNA projects. No rights can be derived from the content. DCNA is not liable for the content and the in(direct) impacts resulting from publishing this article.
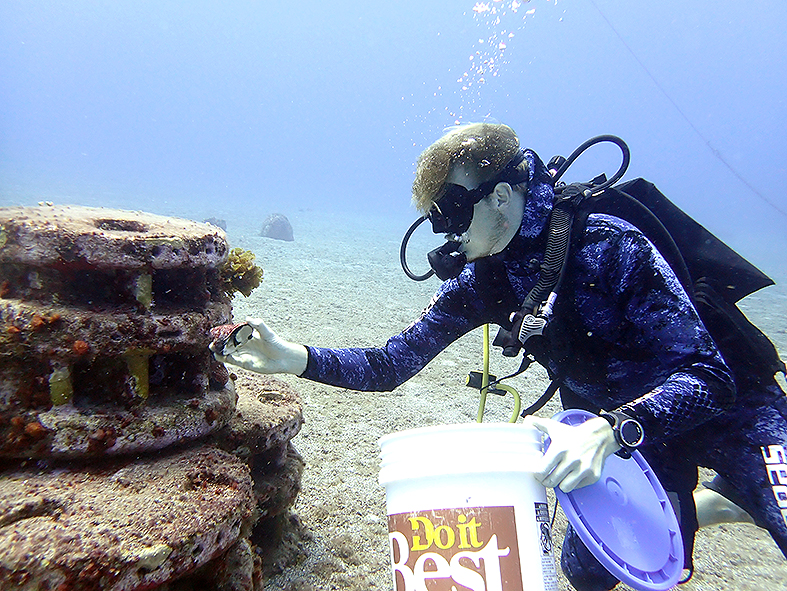

Researcher introducing West Indian top shell (whelk) on artificial reef. Photo credit: Alwin Hylkema
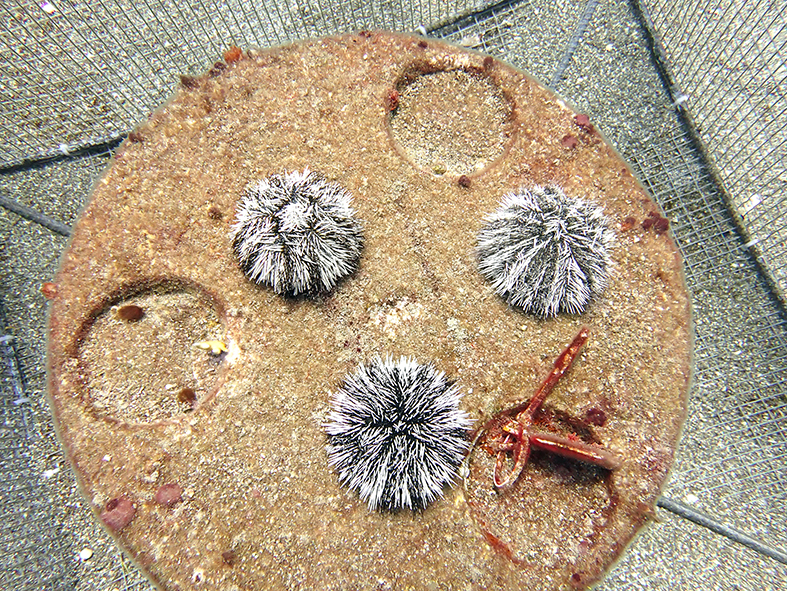

West Indian sea eggs on a Moreef, a modular restoration reef. Photo credit: Alwin Hylkema
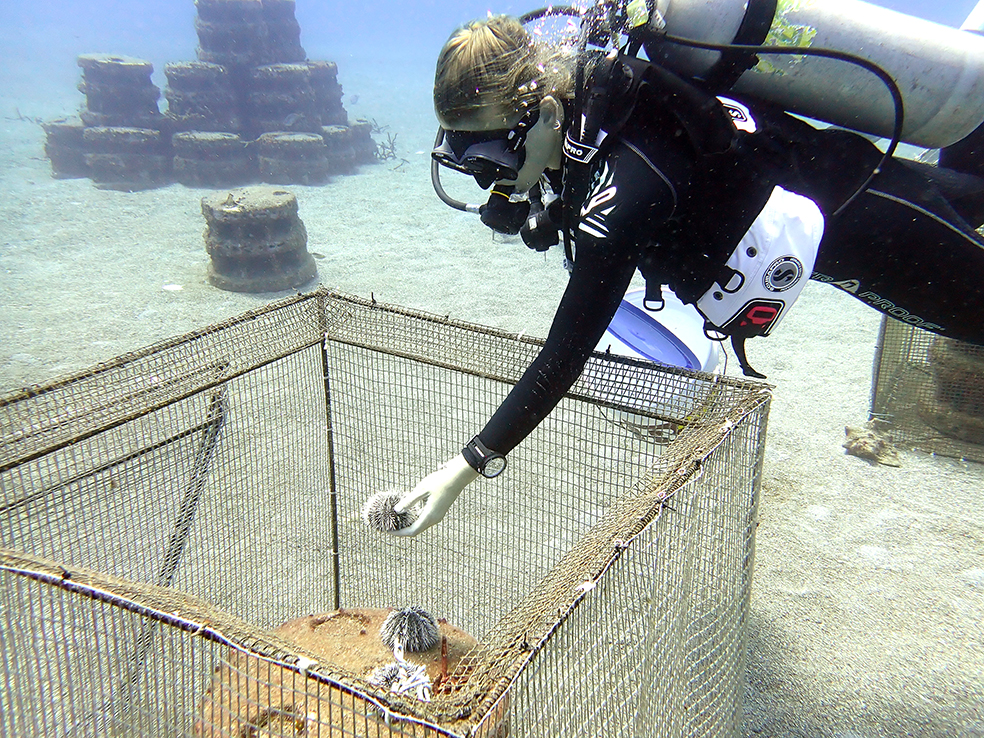

Researcher introducing West Indian sea egg on an artificial reef. The reef is caged to measure the effect of the grazer on the algae. Photo credit: Alwin Hylkema